Himachal Pradesh
Tabo
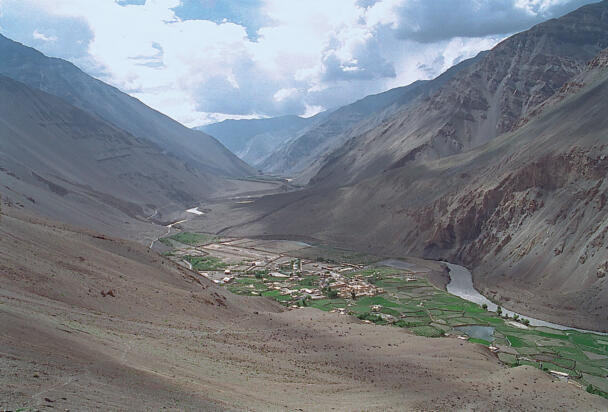
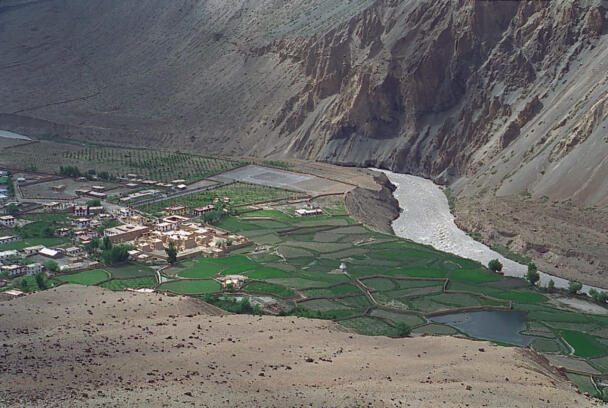
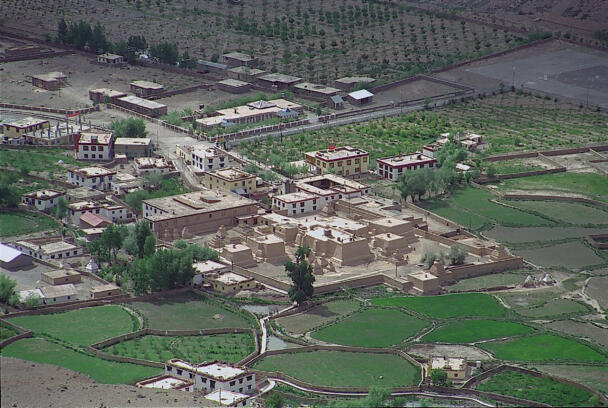
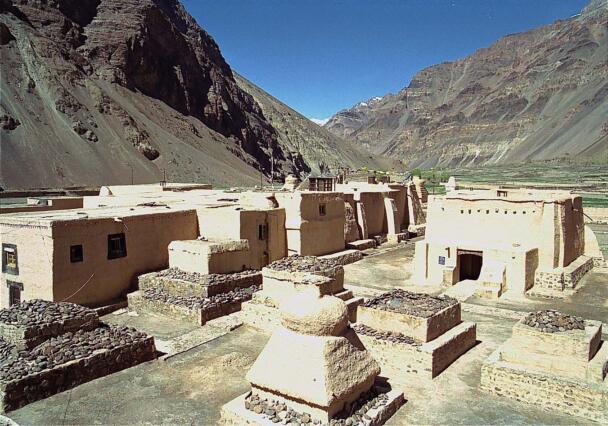
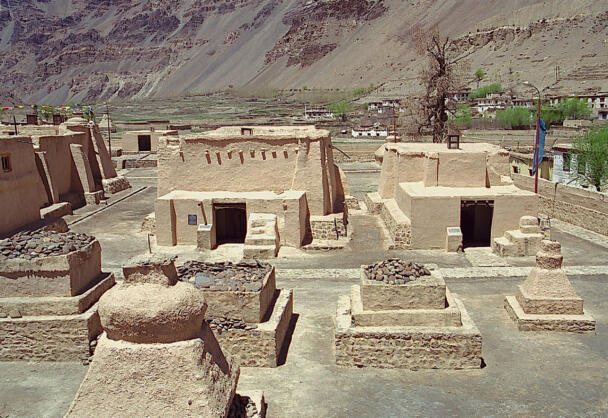
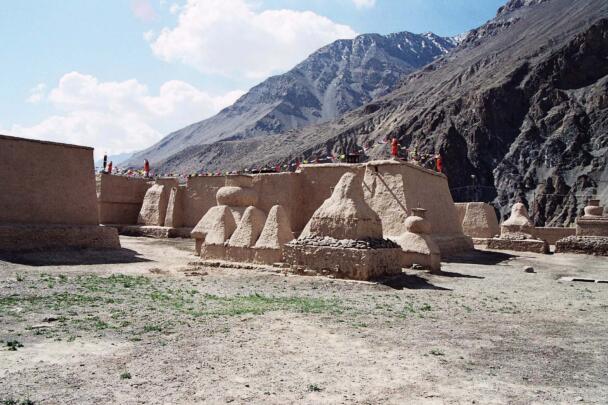
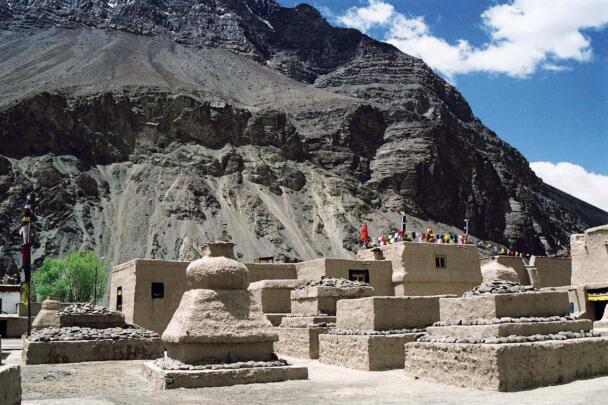
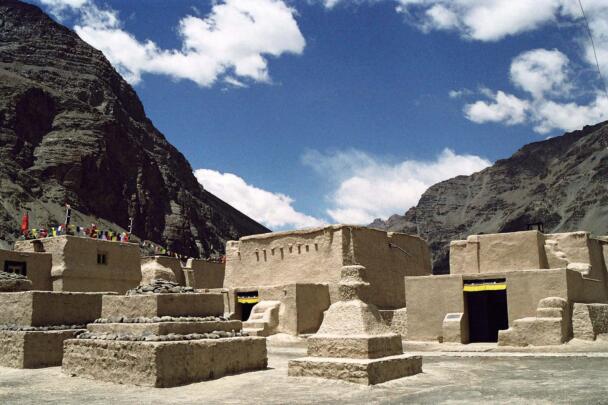
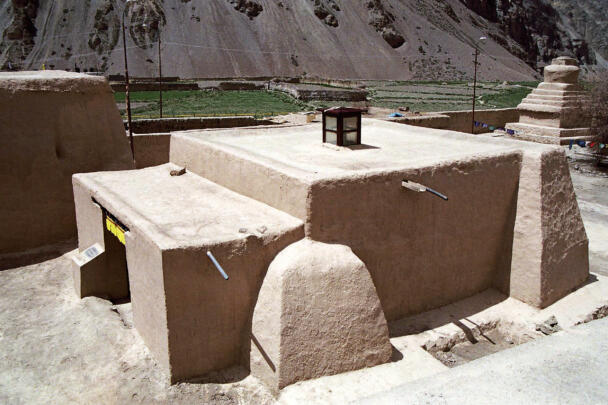
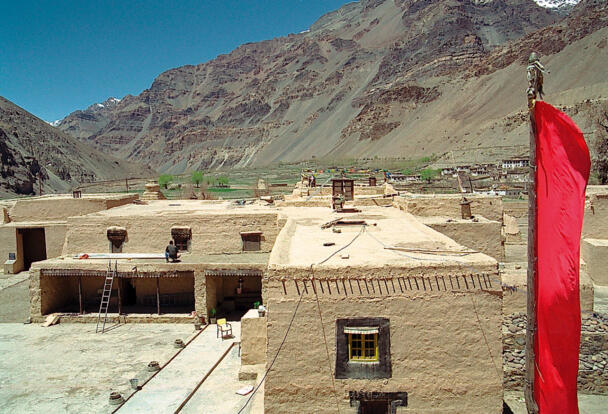
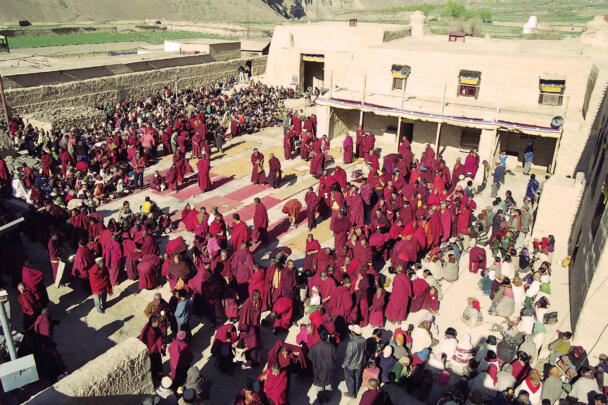













The temple complex of Tabo
Coordinates of the site: 32° 5’36.96″ northern latitude and 78°22’55.50″ eastern longitude, at an altitude of 3285 meters.
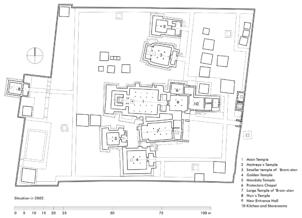
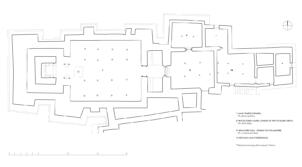
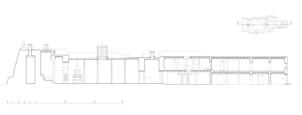
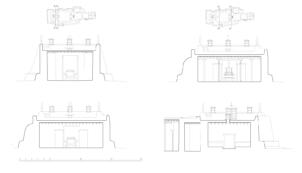
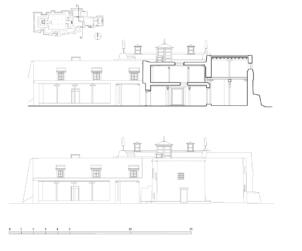
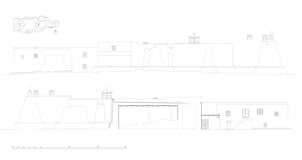
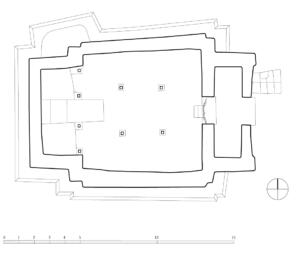
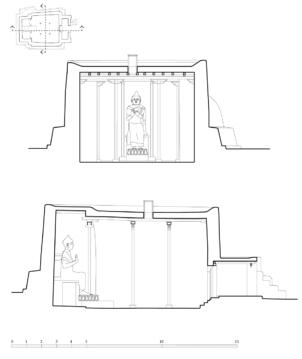
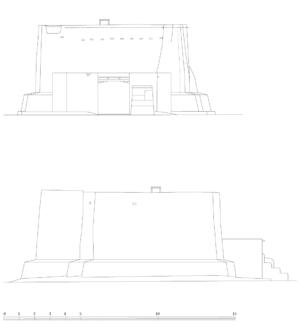
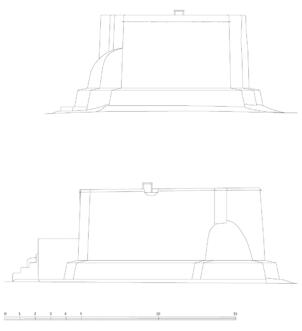
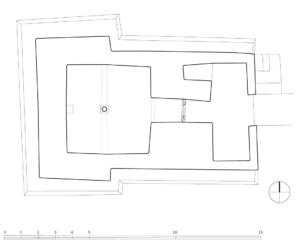
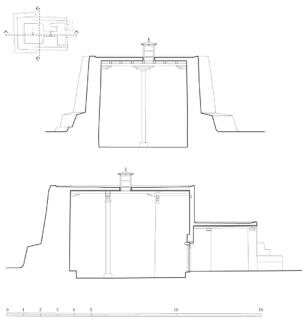
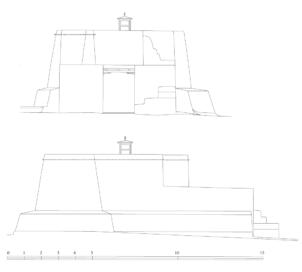
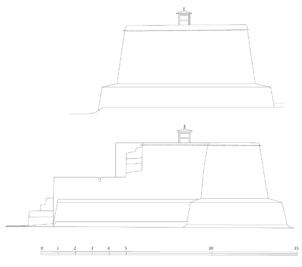
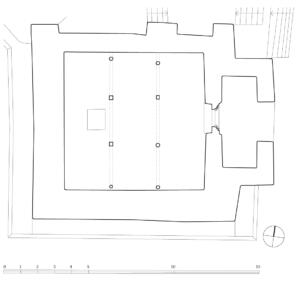
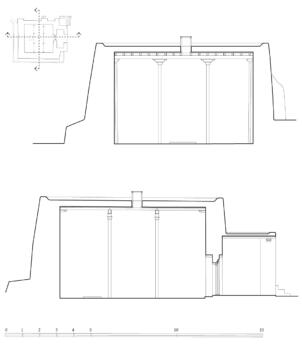
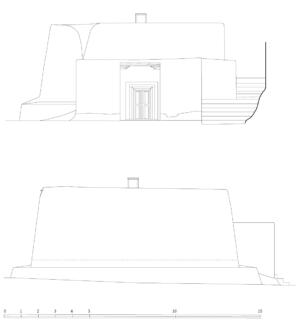
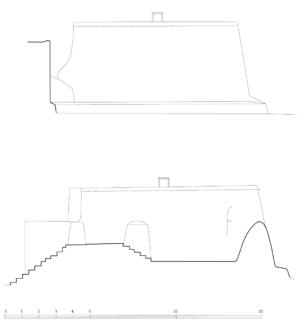
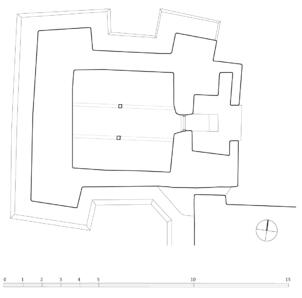
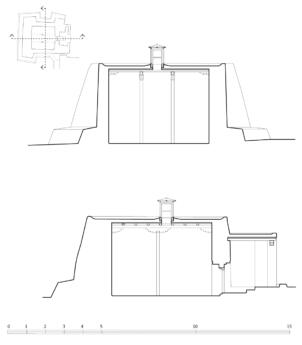
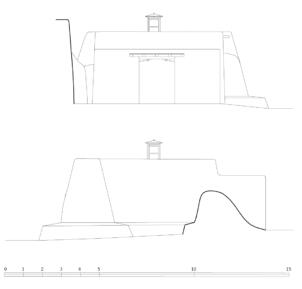
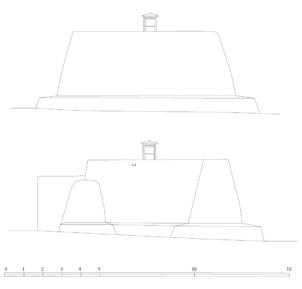
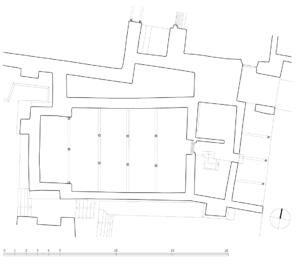
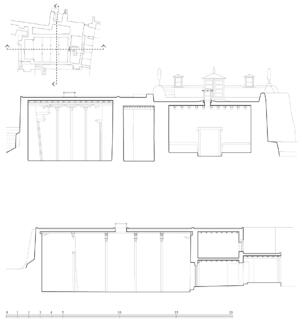
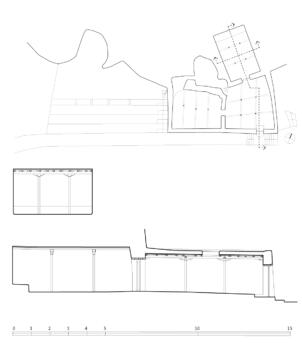
The village of Tabo is located in the lower Spiti valley, about 160 kilometres (airline) north-east of Shimla, the capital of the northernmost Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. Tabo is located on the northern banks of the Spiti river. The area lies in a wide plain of farmland, flanked by mountain ranges. The extensive temple complex is situated in the southwest of the village. Tabo is the oldest Buddhist monastery in India that is still in use. Its original decoration and iconographic artwork are intact. For this reason it was the first monastery in the Western Himalayas to catch the attention of extensive scholarly research. The temple complex consists of nine temples from different periods which are surrounded by a high wall that encloses an almost rectangular area of about 6700 square meters. Of the nine temples within the sacred enclosure only the Main Temple is attributable to the earliest period of Buddhism in the 10th century, while the other temples range from the 14th to the 19th century. The Main Temple (no. 1) is located in the centre of the complex. It consists of a small entry hall, an assembly hall and a cella which is surrounded by an ambulatory. Both the main axis and the original entrance are almost precisely orientated in an east-west direction, deviating with only 3° to the south. The central axes of the other temples vary slightly, between +7° and -8°, from the orientation of the Main Temple. The meaning of these deviations is yet to discover. The building documentation shows that the Main Temple (no. 1) originally was isolated whereas today it is connected with the Protector’s Chapel (no. 6), the New Entrance Hall (no. 9), the adjoining rooms in the east (no. 10) and with the large ‘Brom-ston Temple (no. 7) in the south. Apart from the room structure the walls differ drastically from each other in terms of thickness. The walls of the oldest parts are 115 centimetres thick while the more recent structures, like the walls of the Protector’s Chapel and the Large ‘Brom-ston, range between 50 and 80 centimetres. The latest renovations reinforced some parts of the outer walls, for example the western wall and at the corners of the Main Temple. The sections of the Main Temple show the complexity of the rooms with their different heights ranging between 4.40 metres and 5.10 metres. Additionally the sections depict how the different parts of the Main Temple are illuminated naturally through lanterns in the ceilings. The Main Temple is single storeyed, whereas the later added structures are two-storeyed: the Protector’s Chapel (no. 6), the New Entrance Hall (no. 9) and the adjoining rooms in the east (no. 10) with ceiling heights between 2.10 m and 2.40 metres. As a result of the plan documentation the building phases of the complex and the changes can be determined.
Also see: Dimensioned plan drawings of Tabo. Repository TU Graz, 2024.
Official website of the monastery: Association Serkong Tsenshap International.
Cf. Neuwirth & Auer 2021: The Ancient Monastic Complexes of Tholing, Nyarma and Tabo, pp.168–309, Open Access E-Book. Cf. Luczanits, Christian. 2004. Buddhist Sculpture in Clay: Early Western Himalayan Art, late 10th to early 13th centuries. Chicago: Serindia Publications, pp. 33–56.
2D plans

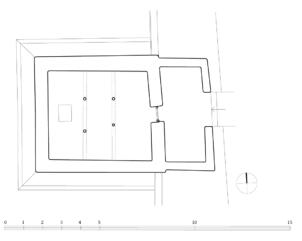
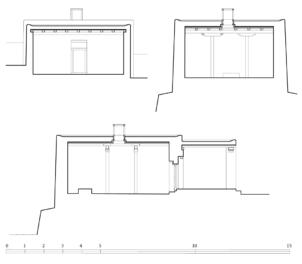
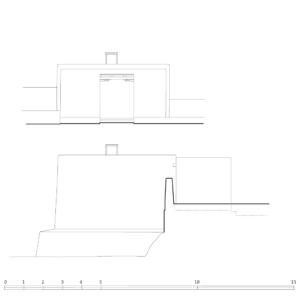
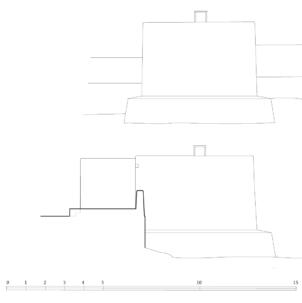
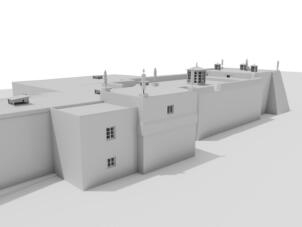
3D Model






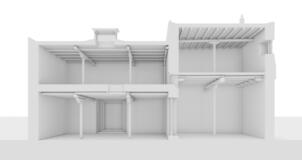

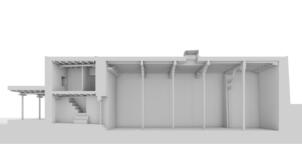

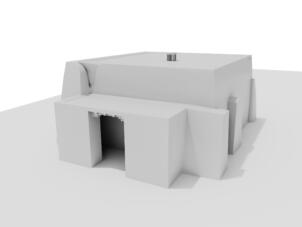
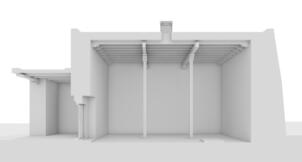

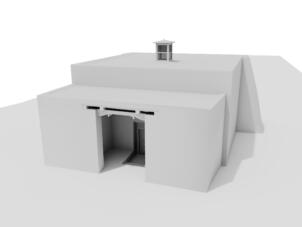
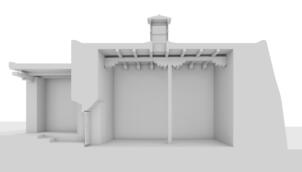

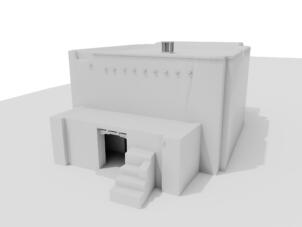
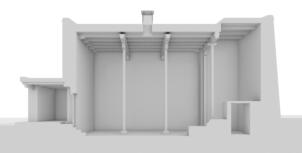

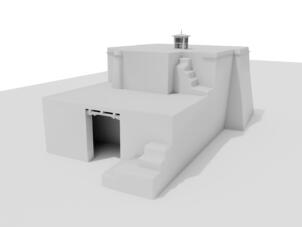
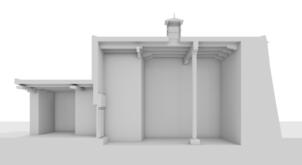

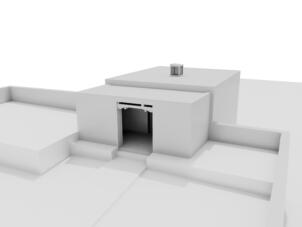
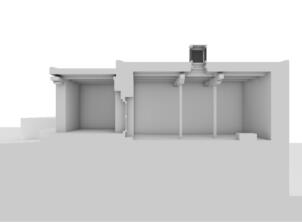
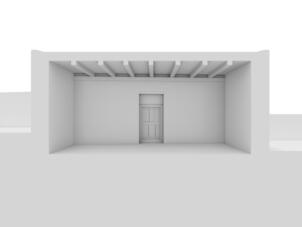

Photomontages of the interior


















Building phases of the monastery












Interior of the Main Temple









More from


